Context
The advent of blockchain technology has revolutionized various sectors, ranging from DeFi and GameFi to Web2 brands like Nike for digital fashion and Starbucks for customer loyalty. However, one area that has remained largely unchanged is physical infrastructure.
Traditionally, the deployment and management of physical infrastructures, such as telecommunications networks, cloud services, mobility networks, and power grids, have been dominated by large companies due to their enormous capital needs and the logistical challenges they pose.
As a result, these companies have maintained a near-monopoly over pricing, conditions, and services offered to end-users, leading to a lack of competition and innovation, until blockchain and Web3 came into the picture and offered a healthier alternative!
Origin of DePIN
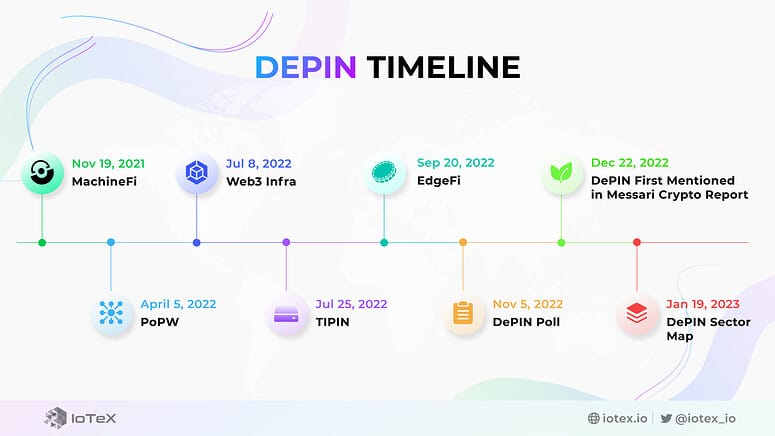
In November 2021, IoTeX became the first Web3 project to name this emerging economy, calling it MachineFi.
Token-Incentivized Physical Infrastructure Networks (TIPIN) emerged the same month.
Then, in August 2022, the Proof of Physical Work (PoPW) concept appeared, referring more specifically to incentive structures allowing anyone to contribute permissionlessly to a set of shared goals.
In September 2022, EdgeFi emerged as a variant of decentralized infrastructure networks focused on deploying hardware resources closer to end-users, at the network's edge. In essence, EdgeFi is a decentralized infrastructure network that prioritizes edge computing.
In November 2022, Messari decided it was time to name Web3's physical infrastructure and conducted a Twitter poll where voters had to choose between PoPW, TIPIN, EdgeFi, and DePIN. The term DePIN won!
What Are We Talking About?
To begin, it's crucial to define a few concepts before diving deeper. Indeed, it's important to revisit some basics and distinctions to understand the relevance of the project in the rest of the post.
What is a DePIN?
"DePIN," which stands for "Decentralized Physical Infrastructure Networks," represents a revolution in how we design and interact with essential physical infrastructures.
They use blockchain technology to create networks where each participant can contribute to and benefit from the collective infrastructure.
The idea is to involve more small players by asking them to provide some of their resources (such as storage, energy, computing power, etc.). In return, these players are "incentivized" with cryptocurrency.
DePINs are often represented by the Network Flywheel:

The Flywheel model allows DePIN projects to grow rapidly and exponentially.
Each new contribution strengthens the entire infrastructure, attracting new users and contributing to constant evolution. This growth dynamic is a key component of DePINs' ability to reshape traditional infrastructures.
This solution allows for better optimization of "fungible" resources, whether it's computing power, energy, or data, among others. In turn, these resources are either directly consumed by businesses or, more often, leveraged in their own products and services.
For example, decentralized networks like Hivemapper sell data directly to transport companies like Uber, which then use the data to improve their product offerings.
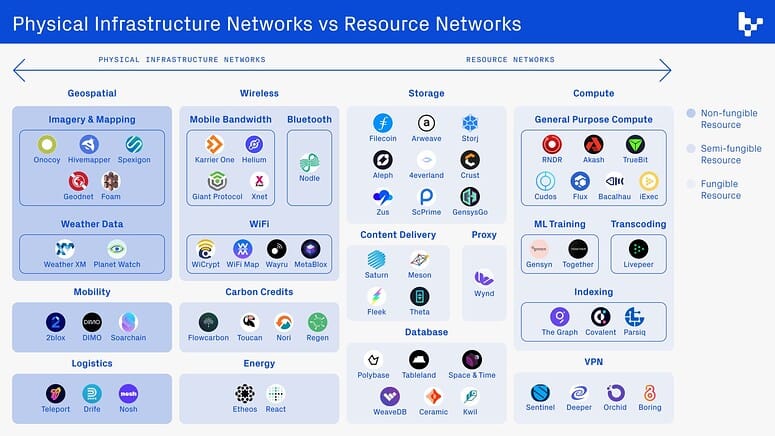
Here is an image of the landscape of consumer-oriented DePIN projects:

DePIN vs DeREN
It is important to distinguish between two main principles, as shown in the figure above. DePINs are different from DeRENs!
Decentralized Physical Infrastructure Networks (DePIN): Crypto-networks with consumable and non-fungible resources that leverage incentives to deploy location-dependent hardware devices.
Decentralized Resource Networks (DeREN): Crypto-networks that use incentives to create marketplaces and increase the supply of existing or unused consumable and fungible resources, relying on location-independent hardware.
DePINs differ from DeRENs in three essential ways:
Fungibility of Resources
Deployment of Location-Based Hardware
Creation of Resources

Below is an overview of the key projects in the DePIN and DeREN sectors:
What is DePIN DAO?
DePIN DAO is a decentralized data center based on the Solana blockchain. It analyzes and integrates user data related to their behavioral habits and provides it to web2 and web3 application service providers.
DePIN DAO uses oracles, and developers, as well as large application development companies, can request data through paid APIs.
Users can upload their own consumption information, such as food, driving, and hotels, and receive DePIN tokens after authentication.
The project can also share its own collected data through oracles, including weather data, environmental data, and traffic data, among others.

What is the Value Proposition?
Today, the data market is unfortunately dominated by a few companies, notably the GAFAM.
Three major problems are encountered in accessing data:
Costly for Businesses: While some data is generally free for consumers, businesses pay a high price to integrate consumer data into their products. With so few reliable data options available, monopolistic pricing makes it difficult for companies and independent developers to afford data.
Almost Inaccessible: Generally, traditional data collection methods are very expensive, making it difficult even for well-funded companies to scale and achieve global reach.
Uncompensated Data: Modern companies rely on large amounts of user-generated data. Many app development companies collect data from users without compensation. In some cases, users are unaware of how their data is being monetized.
To address these issues, DePIN DAO relies on four fundamental elements that allow it to innovate far beyond what centralized networks can offer:
Physical Infrastructure: DePIN networks require physical infrastructure to operate. This could include vehicles for mobility networks, solar panels and batteries for energy networks, access points and routers for wireless networks, or servers for cloud networks.
Off-Chain Computing Infrastructure: DePINs rely on middleware that connects the physical world with blockchain. User activities in the real world are factored into the calculation and distribution of rewards. Additionally, this data can be aggregated for on-chain use cases, such as data proofs for smart contracts and decentralized data marketplaces.
Blockchain Architecture: Each DePIN network interacts with a blockchain architecture containing smart contract logic. This blockchain network acts as a ledger, rewarding transactions and other exchanges of value among network members, such as purchasing broadband access from someone renting their router.
Token Incentives: Supply-side participants are incentivized to join and contribute to the network through token rewards. These tokens serve as a subsidy for supply-side participants, allowing them to develop the network before it generates sustainable fees from demand-side usage.
In summary, the decentralized nature of the project reshuffles the current management of big data and the overall economy of this sector, which could make even the largest data giants tremble.
Similarly, small players can participate in this physical infrastructure. Clearly, it is thanks to blockchain technology that such a democratizing initiative is possible.
Although the project is very captivating and ambitious, implementing a fully decentralized infrastructure that records all information in real-time on a blockchain, which is then stored immutably and used to trigger token-based incentives within a digitalized economy built for this purpose, will be even more challenging.
This project presents a massive challenge, but it is within the reach of the most ambitious!
Tokenomics
The token for this solution is DePIN, with a total supply of 100,000,000 DePIN tokens. There is no price for this token yet as it has not been listed on the market, so don't be surprised.
Let's move directly to the tokenomics, which is very simple:

In summary, 75% of the tokenomics is allocated to users as rewards for their participation in building the DAO.
Next, 20% of the tokenomics goes to the initial investors to provide the necessary startup capital for launching DePIN DAO (such as venture capital, among others).
Finally, 5% is allocated to the DAO's treasury, which helps manage and ensure the success of the DAO.
What's Next?
Currently, the project is in its early stages, but it already has major partnerships:

The two directors of this project come from top American universities and have extensive experience in Big Data:

Marina Karanova specializes in the business aspect of the project, while Jake Nguyen focuses on the technical application. This is a young project within a new narrative, so one should remain cautious, even though the initial promise is quite commendable.
New Narrative
Although DePIN is an emerging sector in cryptocurrency, its growth potential is enormous because this model is used to build better networks in diverse and extensive fields such as telecommunications, energy, mobility, and storage.
While the global real economy is easily valued in the hundreds of trillions of dollars, Messari recently reported that the total addressable market for the DePIN sector is currently $2.2 billion and could reach $3.5 billion by 2028.
This represents about 3x the current market capitalization of the entire cryptocurrency sector. The fully diluted valuation (FDV) of all decentralized physical infrastructure projects is currently only around $5.5 billion.
DePIN projects aim to address some of the world's most fundamental problems by leveraging blockchain technology, token incentives, and the power of the Internet, among other factors.
Conclusion
Most people are familiar with DeFi, GameFi, SocialFi, and DAOs. DePINs represent an increasingly prevalent real-world use case, yet remain relatively unknown. They use tokens to initiate the deployment of physical infrastructure and then create a network effect that unlocks the new design space of real-world-based DApps.
DePINs are an emerging crypto trend that leverages blockchain technology to build and operate physical infrastructures and hardware networks in the real world, in a permissionless, trustless, and programmatic manner.
These DePINs are undoubtedly the next evolution of IoT for the Web3 ecosystem, or a decentralized IoT where users and businesses can monetize data and participate in this market.
They allow individuals around the world to collectively build, maintain, and operate networks of physical infrastructure owned by individuals, without needing a single centralized entity.
They incentivize supply-side participants to build the network using crypto-economic protocols, offering end-users more cost-effective and innovative services than traditional models.
DePIN DAO presents an ambitious project within this promising new narrative. However, as this is a new narrative and an early-stage project, it is essential to be very vigilant and stay informed about the project's progress.

